Standard Email Protocols: SMTP, POP3 & IMAP
What is POP3?
Post office protocol 3 (POP3) is the email protocol that allows users to retrieve email messages from their mail server. POP3 is one of many protocols used by email servers, and it was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
When you use POP3, you connect to your email account through your web browser and download your messages. This means that you can access your messages from anywhere—as long as you have an internet connection.
POP3 was designed for personal users who only need to read and send emails on their devices.
How does POP3 Work?
It was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO),and it's been around since 1986.
The point of POP3 is to allow you to check your email from anywhere in the world, as long as you have an internet connection and an email client that supports POP3.
When you use POP3, you're basically setting up an ongoing conversation between your computer and the email server that holds your incoming messages. When you connect to this server, it downloads all of your new messages from the server and stores them on your computer until you disconnect from it or delete them manually with special commands in your email client software.
In order to use POP3, you must first set up an account with your email provider. You can then download your email to your computer using the POP3 protocol. Your inbox will keep track of how many messages you have downloaded, so if you want to stop downloading new messages, you can delete them from your inbox.
POP3 can be used with or without SMTP
With SMTP
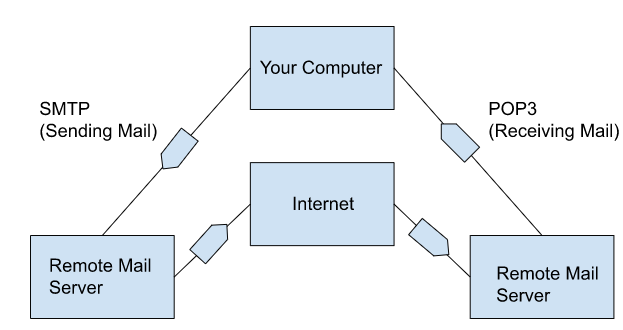
Without SMTP
What is IMAP?
IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol. It's a protocol that allows you to access your mail from multiple devices. It's also known as "Internet mail access protocol," which is why you might see it referred to as IMAP4.
The main benefit of IMAP is that you can use your email on any device—no matter where you are or what kind of computer or phone you have. This means that when you get an email while at home on your laptop, it will show up on your phone too (assuming it's connected to the internet).
How does IMAP work?
It works by keeping all your messages in sync across all devices. This means that when you check your email on one device, the message will also be marked as read on all other devices where you have IMAP enabled. This can be especially helpful if someone sends you an important message while you're at work and then asks if you saw it when they're home later that evening.
It also means that if someone else deletes a message from one device, it will disappear from every other device for which it was synced automatically!
What is SMTP?
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, or SMTP, is the protocol that allows you to send emails from your computer or mobile device. It's how Gmail, Outlook, and other popular email services work.
SMTP is a network protocol for sending emails over the internet. It's designed to allow computers and other devices to communicate with each other over the internet—and it's also what makes sending emails possible in the first place!
Why was it created?
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a standard for sending emails from one server to another. SMTP was designed as an alternative to the Post Office Protocol (POP) and the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP),which were created in 1982 and 1987 respectively.
SMTP is an open protocol, meaning that anyone can use it without paying any licensing fees. It's also one of the oldest TCP/IP protocols still in use today.
A typical email exchange will involve three parties: a sender, a receiver, and a mail transfer agent (MTA). The sender sends an email message to the receiver's MTA using SMTP commands. The MTA then delivers that message to the receiver's computer.
How does SMTP work?
SMTP works by sending a message to an SMTP server, which then sends it to another SMTP server until it reaches its destination. This means that all your emails are being sent through several different servers along their journey from your computer to their destination.
There are three main components required for an SMTP connection:
- The sender (you)
- An SMTP server that will send the message on its journey
- A recipient - this could be another person or an email server
To send an email using SMTP, you need:
-Your email address, which might be something like "[email protected]"
-Your password (if you're using an account with two-factor authentication enabled)
-The address of your recipient's email server (their SMTP server),which is usually something like "mail.example.com"
SMTP, POP3, and IMAP: How Are They Related?
To summarize:
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It's used to send messages from one computer to another over the Internet.
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol 3. It's used to download emails from an email server onto a local computer.
IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol. It's used to access email on an email server from any device.
Well, if you've ever dealt with email before, you know that there are three main ways to send it: through a server, through a web app (like Gmail),or through an email client like Outlook or Apple Mail.
When you use a server like Gmail to send an email, your computer sends the message to Gmail's server over port 25 (SMTP). The message gets forwarded to the recipient's email address through port 110 (POP3) or 143 (IMAP). The recipient can then download it from their own email client, which connects to the server over port 110 (POP3) or 143 (IMAP) as well.
So yes, SMTP is used by your mail client when sending mail and receiving it from the server; POP3 and IMAP are used by your mail client when getting messages from the server.
Standard Email Protocols: SMTP, POP3 & IMAP Free4 m
What is Email Security? Free4 m
Email Security Practices Free4 m
Building an Email Security Compliance Model Free5 m
Corporate Email Security Checklist Free3 m 30 s
What is the difference between Inbound email security and outbound email security? Free4 m
What is Information Security? Free4 m
Zero Trust Security Model Free3 m
What is SPF Alignment? Free3 m
How to Set Up Microsoft Office 365 SPF record? Free4 m
How to Set Up Google Workspace SPF Record? Free2 m
How to Set Up MailChimp SPF Record? Free3 m
How to Set Up SendGrid SPF Record? Free2 m
How to Set Up Salesforce SPF Record? Free3 m
How to Setup Zoho Mail SPF Record? Free2 m
What is DMARC Compliance? Free2 m
The Benefits of DMARC Free2 m
DMARC Configuring Free3 m
Achieving DMARC Enforcement Free2 m
DMARC Vs Antispam Solutions Free2 m
DMARC Identifier Alignment Free2 m
DMARC sp Tag Exceptions & Uses Free1 m
Configuring DMARC without DKIM Free3 m
Configuring DMARC without SPF Free2 m
DMARC Aggregate Report Views Free3 m
Video - PowerDMARC Aggregate Reports Free2 m 13 s
DMARC Forensic Report Views Free2 m
Video - PowerDMARC Forensic Reports Free
DMARC Forensic PGP Encryption and Decryption Free2 m
TLS Report Views Free3 m
Video - PowerDMARC TLS Reports Free
PDF/CSV Reports Free2 m
Video - PowerDMARC PDF/CSV Reports Free1 m 1 s